MCM: The Mathematical Contest in Modeling
ICM: The Interdisciplinary Contest in Modeling
2000 Mathematical Contest in Modeling
The Problems
Problem
A: Air traffic Control
Problem
B: Radio Channel Assignments
Problem A Air traffic Control
Dedicated to the memory of Dr. Robert Machol, former chief
scientist of the Federal Aviation Agency
To improve safety and reduce
air traffic controller workload, the Federal Aviation Agency
(FAA) is considering adding software to the air traffic control
system that would automatically detect potential aircraft
flight path conflicts and alert the controller. To that end,
an analyst at the FAA has posed the following problems.
Requirement A: Given two airplanes flying in space,
when should the air traffic controller consider the objects
to be too close and to require intervention?
Requirement B: An airspace sector is the section of
three-dimensional airspace that one air traffic controller
controls. Given any airspace sector, how do we measure how
complex it is from an air traffic workload perspective? To
what extent is complexity determined by the number of aircraft
simultaneously passing through that sector (1) at any one
instant? (2) during any given interval of time?(3) during
a particular time of day? How does the number of potential
conflicts arising during those periods affect complexity?
Does the presence of additional software tools to automatically
predict conflicts and alert the controller reduce or add to
this complexity?
In addition to the guidelines for your report, write a summary
(no more than two pages) that the FAA analyst can present
to Jane Garvey, the FAA Administrator, to defend your conclusions.
Problem B
Radio Channel Assignments
We seek to model the assignment of radio channels
to a symmetric network of transmitter locations over a large
planar area, so as to avoid interference. One basic approach
is to partition the region into regular hexagons in a grid
(honeycomb-style), as shown in Figure 1, where a transmitter
is located at the center of each hexagon.
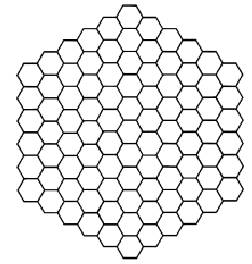
Figure 1
An interval of the frequency spectrum is to be allotted for
transmitter frequencies. The interval will be divided into
regularly spaced channels, which we represent by integers
1, 2, 3, ... . Each transmitter will be assigned one positive
integer channel. The same channel can be used at many locations,
provided that interference from nearby transmitters is avoided.
Our goal is to minimize the width of the interval in the frequency
spectrum that is needed to assign channels subject to some
constraints. This is achieved with the concept of a span.
The span is the minimum, over all assignments satisfying the
constraints, of the largest channel used at any location.
It is not required that every channel smaller than the span
be used in an assignment that attains the span.
Let s be the length of a side of one of the hexagons.
We concentrate on the case that there are two levels of interference.
Requirement A: There are several constraints on frequency
assignments. First, no two transmitters within distance 4s of
each other can be given the same channel. Second, due to spectral
spreading, transmitters within distance 2s of each other
must not be given the same or adjacent channels: Their channels
must differ by at least 2. Under these constraints, what can we
say about the span in,
Requirement B: Repeat Requirement A, assuming the
grid in the example spreads arbitrarily far in all directions.
Requirement C: Repeat Requirements A and B, except assume
now more generally that channels for transmitters within distance
2s differ by at least some given integer k, while those
at distance at most 4s must still differ by at least one. What
can we say about the span and about efficient strategies for designing
assignments, as a function of k?
Requirement D: Consider generalizations of the problem,
such as several levels of interference or irregular transmitter
placements. What other factors may be important to consider?
Requirement E: Write an article (no more than 2 pages)
for the local newspaper explaining your findings.
|

